Contents
How Amino Acids Boost The Immune System
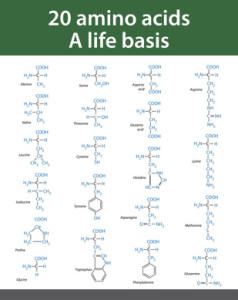
Amino acids are essential organic compounds with a primary function as the building blocks for proteins, which constitute around 16% of our body weight. They are made up of an Amine group, Carboxylic Acid group, as well as a functional side-chain which is specific to each individual amino acid.
You will learn
- The significance of amino acids to the human body
- The two types of immune response by the body
- Which amino acids are particularly important to the immune system
- Which specific conditions can be treated with amino acids
Large Scale Diversity
In total, there are 20 amino acids which are found within proteins. The precise amount of amino acids within the protein as well as the sequence they are expressed in, and the way in which they form bonds with each other and fold into a three dimensional structure, all account for the massive variety seen in the different proteins found in the human body.
However, amino acids also have other important roles in the body, such as as intermediates in metabolism, catalysts for most of the important reactions in living cells, as well as regulation of the immune system.
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues and organs which protect the human body against attack from foreign bodies, which could potentially lead to illness and disease. The immune system is designed to defend against a wide variety of pathogenic organisms, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasitic worms.
The two main types of immune response are the innate Immune system, and the adaptive Immune system.
Innate Immune system
The Innate response consists of generic mechanisms to destroy invading organisms. Inflammation is a common response which increases blood flow to an infected area, utilizing compounds such as prostoglandins to cause dilation of blood vessels, as well as an increase in body temperature (fever) which hinders the activity of some pathogens and increases the mobility of immune system cells. Other chemical compounds such as cytokines produce “interferons” that act as antiviral agents.
The second line of defense for the Innate system is through the action of leukocytes, or white blood cells. There are a range of different leukocytes, the most abundant being the phagocytes. These are cells which specialize in physically engulfing invading organisms in a process known as phagocytosis, and then destroying them using digestive enzymes. These cells patrol the bloodstream in search of pathogens, but can also migrate to a specific location (such as the site of an injury where infection has started) by reacting to certain chemicals released by the immune system.
All of the aforementioned responses are non-specific, and do not provide long term immunity against a specific pathogen.
Adaptive Immune system
The adaptive immune system provides the body with an immunological memory, allowing it to remember specific pathogens in order to mediate a much faster response should the body be infected again by the same organism. This mechanism uses cells known as lymphocytes, or more specifically, B Cells and T Cells. Pathogens which invade the body carry certain substances called antigens, which are used by lymphocytes to recognize the pathogen as a foreign body. The B cell contains an antibody on its surface, which binds to the antigen to form an antigen/antibody complex. This is taken up into the B cell, processed, and then certain proteins displayed on the cell surface.
These proteins attract matching T-helper cells, which through the release of chemicals known as lymphokines, activate the B cell. After this, the B cells proliferate into plasma cells, releasing a massive quantity of antibodies into the bloodstream, which circulate and bind to the antigens on pathogens and subsequently mark them for uptake and destruction by the previously mentioned phagocytes. Antibodies also serve to destroy pathogens directly, by binding to toxic substances released by them and therefore rendering them ineffective. Some of the B and T cells in the body go on to become long term memory cells, which can instantly recognize specific pathogens and trigger a much faster, stronger response if the same infection occurs in future.
Amino Acids and the Immune System
It is widely accepted that amino acids play a key role in regulating the body’s immune response. Three common amino acids found in the body are glutamine, arginine, and cysteine, and all have been found to have important functions.
In subjects with low plasma glutamine levels, several glutamine-dependent immune responses can be disturbed. These include a reduction in B cell differentiation to plasma cells and a reduced proliferation of T cells. Im general, Glutamine is utilised at a high rate by cells of the immune system in culture and is required to support optimal lymphocyte proliferation and production of cytokines by lymphocytes and macrophages1.
Macrophage-mediated phagocytosis is influenced by glutamine availability and may run inefficiently if Glutamine levels are low.
Arginine
Arginine depletion can also cause suppression of T cell proliferation and impaired T cell functionality.
In the absence of the arginine protein, a lower number of T helper cells contained their surface receptors, as a specific protein chain which is part of the receptor complex requires an adequate amount of arginine molecules.
Reduced numbers of receptors on T cells impairs immune function, as there is less interaction and activation of B cells and so a lower number of antibodies produced.
Cysteine
Cysteine is also important to T cells, as it is a precursor of the tripeptide glutathione.
In order for T cell activation and proliferation to occur, their intracellular glutathione content must be increased to sufficient amounts, and without adequate cysteine levels glutathione synthesis is also subsequently limited.
A lack of protein in the diet can adversely affect the immune system as shown, and specifically have a negative impact on the T cell system. Supplementation of these amino acids can significantly increase one’s capacity to resist infections.
Applications in Treatments
Amino acids also have applications in certain medical treatments. As mentioned above, the effectiveness of T cells in the body’s immune response is highly dependent on certain amino acids, most notably arginine. Supplementing the diet with arginine and increasing the concentration of this amino acid in the body can enhance immune mechanisms, and is specifically used in postoperative surgical patients to return T cell levels to normal.
Controlled Amino Acid Treatment
Some types of cancer can also be treated through the use of Controlled Amino Acid Treatment (CAAT), a purely nutritional approach to targeting cancerous cells. By using a strict diet with a highly specific list of amino acids as well as nutritional supplements, cancer cells can potentially be starved and killed. The treatment interferes with the production of ATP by disrupting glycolysis and preventing cancer cells from obtaining energy, prevents new blood vessel formation, reduces production of growth factors such as HGH which cause cancer cells to proliferate, and reduces the amount of certain amino acids such as glycine which are necessary for DNA replication in cancerous cells.
To achieve this, certain amino acids are provided in relatively high quantities to the patient, whilst others are highly restricted, depending on the specific type of cancer being targeted.
Neurobehavioral disorders
ADD and ADHD are two neurobehavioral disorders which can also be treated through the use of amino acids. Most patients who suffer from these disorders are born with a shortage of neurotransmitters, and also manufacture less of them over the course of their lifetime. This deficiency of neurotransmitters affects the brains chemical balance and can lead to maladaptive behavior.
Neurotransmitters are synthesized from amino acids such as GABA, glycine, taurine, glutamine and tryptophan. Low levels of these amino acids are often found in children with ADD or ADHD, and often supplementing them in specific doses can improve the adverse affects of these disorders. This offers benefits over typical drugs used to combat these conditions, which can be addictive and have dangerous side effects.
HIV
HIV, an immunodeficiency virus, can also be tackled through selective use of amino acids. The majority of people who contract the HIV virus go on to eventually develop the full on AIDS infection, as the virus replicates and severely damages the immune system. Supplementation with a special form of the amino acid cysteine, has been shown to potentially help patients with HIV live longer.
Using a type of cysteine called N-acetylcysteine (NAC) , there is an increase the production of glutathione, which is a natural antioxidant that neutralizes several harmful substances that enter the body.
It is also highly important in regulating and maintaining the health of white blood cells necessary to the body’s immune response. The HIV virus blocks the transport of cysteine into cells, reducing glutathione production, but through the use of NAC which is transported in a different manner and able to bypass this block and enter the body’s cells, patients exhibited healthy levels of glutathione which in turn could help improve immune function and the ability of patients to cope with infections.
Conclusion
Whilst primarily used for building the various proteins which make up the body, amino acids have other essential roles in regulation of the body’s defenses. Deficiencies in certain amino acids can result in decreased immune function and a greater chance of developing serious infections. As a result, it is important to maintain adequate levels of important amino acids in the body. This can be done either purely through a balanced diet or with the use of specific supplements depending on the individual.
Furthermore, amino acids are currently being used to combat certain illnesses and diseases which can affect various bodily systems. They have shown to be increasingly effective in reducing symptoms and helping control disorders without the adverse side effects of addictive drugs and medications.
Biliography
- “https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10582122” ↩